The simplest parasite is an organism that is capable of invading and living in the cells and tissues of other organisms. The simplest parasites cannot live in an open environment on their own like other protozoa, but must penetrate the body of another organism to receive protection and nourishment.
The simplest parasites and their varieties
The simplest organisms are eukaryotic systems that exist as structurally and functionally independent individual cells (including species that form societies or colonies). Protozoa develop relatively complex subcellular properties (membranes and organelles) that allow them to survive harsh environmental conditions. Most protozoa are microscopic organisms, and only a few grow large enough to be visible to the naked eye. They move as unicellular eukaryotes to survive, feed, and reproduce.
There are the simplest parasites that cause problems. They are present in our food, in the soil and in the water, and they can get very sick of us if they ever get into us.
Each protozoan parasite can cause different diseases in our body. Some can cause serious illnesses in the airways (the passage of air from the nose to the lungs) and the central nervous system (brain, cranial nerves, and spinal cord), while others live in the intestines and cause symptoms such as diarrhea and are not fatal.

There are four types of protozoan parasites, which are classified according to their motion:
- sarcodes are a group of amoebas that are static and move through contractions that change the shape of their cells;
- mastigophores move by flagella;
- silophores use cilia;
- sporozoa are immobile when they are in the mature stage.
Life cycles of protozoan parasites
Most protozoa have enormous reproductive potential due to their short generation time, undergo rapid sequential development, and produce large numbers of offspring asexually or sexually. These features are responsible for a multitude of the simplest infections, quickly causing acute symptoms of the disease.
The developmental stages of unicellular parasites that occur within the host usually consist of the feeding of trophozoites and are found intracellularly (within the host cells) or extracellularly (in hollow organs, body fluids, or intercellular internodes). Although trophozoites are ideal for their parasitic mode of existence, they are not very resistant to external environmental conditions and do not live outside their host for long. Protozoan parasites use one of four main modes of transmission to migrate from host to host: direct, fecal-oral, infectious, and predatory.
Ways of transmitting protozoan parasites to humans
- Direct transmission of parasites through intimate contact with the body - sexually (e. g. , Trichomonas talking fungi that cause trichomoniasis in humans).
- Faeces of the ecologically stable stage of cysts —oral transmission — parasites are excreted in one host cavity and transmitted with food or water to another (e. g. , Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia duodenalis, and Balantidium coli to all forms of fecal cysts), which amoebicand balantidiosis).
- Infection occurs when parasites are ingested by blood-sucking arthropods (insects or arachnids) and transmitted by bite to new farmers (e. g. , Trypanosoma brucei, tsetse flies transmitted and cause sleeping disease, and caused by Plasmodium spp. Hemosporidia, mosquitoes, and mosquitoes).
- Transmission from predator to prey occurs when the simplest parasite gets stuck in the victim’s tissues (e. g. , cow, goat, pig) and is eaten by a predator (in our case, a person).
The simplest human parasites and the diseases they cause
Acanthamoeba. This parasite infects the human eye or brain and causes exogenous amoebiasis. You can live in any region of the world. People can get it by cleaning their contact lenses with tap water.
Babesia. It infects red blood cells and causes a disease called babesiosis. Different types of parasites live in different parts of the world. When bitten, ticks are transmitted.
Balantidium (Balantidium coli). It lives in the intestinal mucosa, causing ciliated dysentery, also known as balantidiosis.
Blastocystis (Blastocystis). This parasite infects the intestines of the host. It enters humans through human or animal fecal contaminated, consumed foods. The disease caused by the parasite is called blastocytosis.
Cryptosporidium (Cryptosporidium). It lives in the human gut. It is spread all over the world. It enters the human body through ingested food contaminated with human or animal feces.

Dysentery amoeba (Entamoeba histolytica). This is the simplest parasite that causes intestinal amebiasis. They are most commonly found in densely populated, poorly hygienic and tropical regions. Feces are spread by the oral route.
Giardia lamblia. It lives in the lumen of the small intestine. If people consume food or water contaminated with feces, dormant Giardia cysts can infect the body and cause intestinal giardiasis. It is especially dangerous for children and requires mandatory adherence to treatment regimens.
Isospore (Isospora belli). It affects the epithelial cells of the small intestine. It is spread all over the world. Stool is spread orally and is the pathogen of isospore.
Leishmania. It parasitizes human skin and internal organs. It exists worldwide in various forms. Certain types of mosquitoes transmit when biting.

Negleria (Naegleria fowleri). It causes primary amoebic meningoencephalitis because it lives in the human brain. Infection occurs through contaminated soil, swimming pools, and contaminated water.
Plasmodium (Plasmodium falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale, P. malariae). Parasites enter red blood cells and cause malaria. They exist in tropical areas where Anopheles, also known as anopheles mosquitoes, are carried.
Rhinosporidium seeberi. It multiplies in the nose and nasopharynx, growing there in the form of spores there. It exists in India and Sri Lanka. Swimmers in public waters can become infected with the parasite when the nasal mucosa comes in contact with the contaminated material.
Toxoplasma (Toxoplasma gondii). It affects the liver, heart, eyes and brain. It is a widespread parasite worldwide. People can become infected after consuming raw or undercooked pork, lamb, goat or milk. It can also occur in contaminated food or soil due to cat feces. The disease caused by the parasite is called toxoplasmosis or parasitic pneumonia.
Trichomonas (Trichomonas vaginalis). It infects the female urogenital tract. Symptoms are different in men and women. It is the causative agent of a sexually transmitted infection, trichomoniasis.
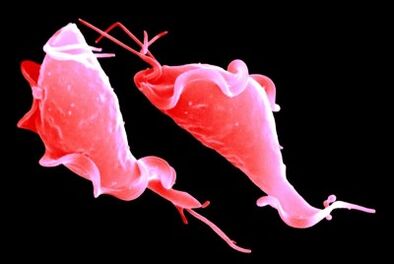
Trypanosomes (Trypanosoma brucei, Trypanosoma cruzi). The first type of parasite affects the central nervous system, blood, and lymphatic system. The chatter fly carries and causes a so-called sleeping sickness. The second parasite causes Chagas disease by affecting the blood, muscles, nerves, heart, esophagus and intestines. They are also transmitted by insect bites.
How to treat infections caused by protozoan parasites in humans?
The treatment plan for protozoan parasitic infection depends on the specific diagnosis. Your doctor will usually prescribe medicines to treat, for example, trichomoniasis, giardiasis or cryptosporidiosis. Generally, medications are not prescribed for toxoplasmosis unless the conditions are in the form of pregnancy, other illness, or a severe and prolonged infection.
Your doctor may suggest other treatments to relieve your symptoms. For example, many parasitic infections can cause diarrhea, which often leads to dehydration. Therefore, when treating an infection caused by protozoan parasites, it is usually recommended to drink plenty of fluids to make up for the loss of the body.
How to prevent protozoan parasites?
There are several steps you can take to reduce the risk of a parasitic infection:
- practice safe sex using a condom;
- wash your hands regularly, especially after handling raw food or feces;
- Cook the food to the recommended seed temperature.
- drink clean water, including bottled water, when you travel;
- avoid swallowing water from lakes, streams or ponds;
- Avoid cat apples and feces during pregnancy.
If you suspect you may have a parasitic infection, ask your doctor for an appointment. They can help diagnose the cause of the symptoms and suggest a treatment plan. The sooner you start treatment, the sooner it can help stop the infection from spreading to others.